Knowledge Centre
How wind energy is shaping Australia’s future

The role of wind turbines in Australia’s energy landscape
Australia is a vast country with enormous potential for renewable energy, and wind power has emerged as a key player in shaping the nation’s energy future. As the world accelerates its transition to cleaner energy sources, wind turbines are becoming an increasingly integral part of Australia’s energy mix.
With its ideal geographical location, Australia boasts some of the best conditions for wind energy generation. Wind farms are spreading across the country, harnessing the power of strong winds to produce electricity, lower emissions, and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Wind energy now supplies a significant portion of Australia’s electricity needs and is expected to continue growing in the coming decades.
This article will explore how wind energy works, the environmental benefits of wind turbines, key projects and wind farms across the nation, and the future of wind energy in Australia.
How wind energy works and its environmental benefits
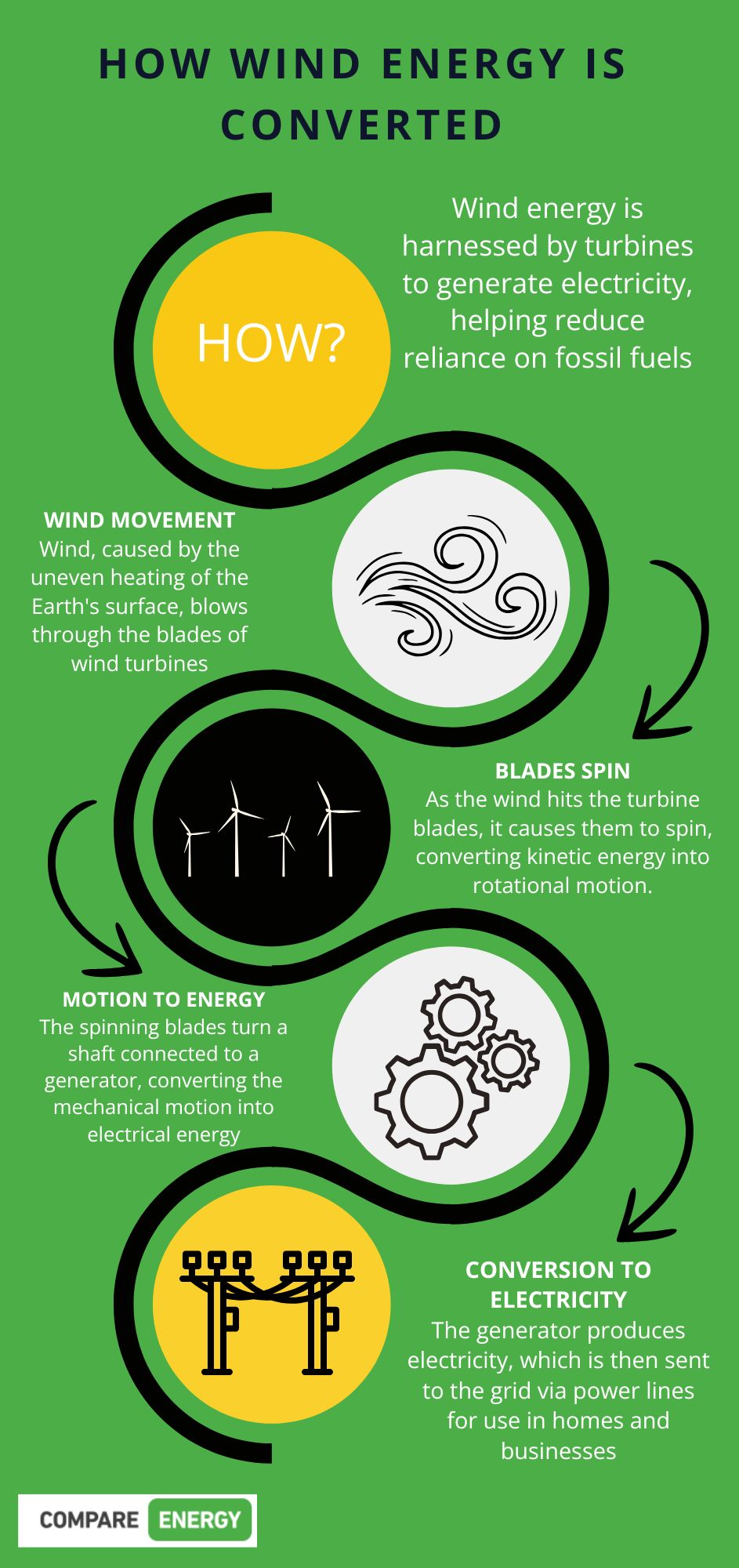
Wind energy is generated by harnessing the power of moving air through wind turbines. These turbines consist of large blades that spin when the wind blows, converting kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then converted into electrical energy using a generator.
Wind turbines can be grouped into two main types:
- Onshore wind turbines: These are located on land, typically in areas with strong, consistent winds, such as coastal regions or inland plains.
- Offshore wind turbines: These are placed in bodies of water, usually along the coast, where wind speeds are higher and more consistent.
Wind energy is often referred to as "clean energy" because it produces no direct emissions during the generation process. Unlike fossil fuel-based power stations, which emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases, wind power is a renewable energy source that helps reduce the environmental impact of electricity generation.
Environmental benefits of wind energy
Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Wind turbines produce zero emissions during operation, helping to mitigate climate change by reducing the carbon footprint of electricity production. Over their lifetime, a single wind turbine can offset hundreds of thousands of tonnes of CO2 that would otherwise be emitted by coal or gas-fired power plants.
Conservation of water resources
Unlike coal, natural gas, or nuclear power stations, wind energy does not require water for cooling purposes. This is particularly valuable in Australia, where water scarcity is a major issue.
Biodiversity protection
Wind farms help to reduce habitat destruction associated with mining and fossil fuel extraction. Additionally, when properly sited, wind turbines have a relatively low impact on local wildlife compared to traditional power plants.
Reduction of air and noise pollution
Wind turbines do not produce harmful air pollutants such as sulphur dioxide (SO2) or nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are associated with fossil fuel combustion. Additionally, while there can be noise generated by the turbines, it is generally much less disruptive than that of conventional power plants or factories.
Sustainability
Wind is a renewable resource, meaning it will never run out as long as there are breezes to harness. This makes wind energy a sustainable solution for powering communities and industries over the long term.
Key wind turbine projects and wind farms in Australia to note
Australia has invested heavily in wind energy, and there are numerous notable projects and wind farms across the country that are shaping the future of clean power generation. Here are some key wind farms to keep an eye on:
Ararat Wind Farm (Victoria)
Located in the Wimmera region of Victoria, the Ararat Wind Farm is one of the largest in Australia. With a total generating capacity of 240 MW, this wind farm features 75 turbines and supplies clean electricity to over 100,000 homes. It was officially opened in 2017 and is a key contributor to Victoria's renewable energy efforts.
The project was developed as part of the state’s strategy to diversify its energy mix and reduce emissions. The farm’s large-scale production has significantly boosted local economic growth, creating jobs and supporting regional infrastructure.
Boco Rock Wind Farm (New South Wales)
The Boco Rock Wind Farm is located in the Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, with an installed capacity of 113 MW. This wind farm includes 46 turbines and has been generating renewable electricity since 2014.
It plays a critical role in supporting NSW’s energy transition to a low-carbon future, and it is part of a larger investment in renewable energy infrastructure across the state. The project also benefits local communities by providing long-term employment opportunities and contributing to the region’s economic development.
Cathedral Rocks Wind Farm (South Australia)
Situated on the Fleurieu Peninsula, Cathedral Rocks Wind Farm has a generating capacity of 119 MW. The farm features 46 turbines that harness the strong coastal winds typical of the region. This wind farm has been in operation since 2009 and is one of South Australia’s early success stories in renewable energy.
It produces enough power to supply over 70,000 homes, contributing significantly to South Australia's position as a leader in wind energy generation. Cathedral Rocks also showcases how wind energy can integrate seamlessly with the state’s existing grid, contributing to the state’s ambitious renewable energy targets.
Collgar Wind Farm (Western Australia)
Located in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia, the Collgar Wind Farm boasts a capacity of 206 MW, making it one of the largest wind farms in the state. Comprising 111 turbines, it has been operational since 2012 and is capable of supplying around 120,000 homes with clean energy annually.
Collgar is a significant contributor to Western Australia's growing renewable energy sector and plays a vital role in supporting the state's shift towards sustainability. In addition to generating electricity, Collgar helps the region by providing local employment and contributing to the development of renewable energy infrastructure.
Coopers Gap Wind Farm (Queensland)
Located in Queensland’s Darling Downs region, the Coopers Gap Wind Farm is one of the newest and largest wind farms in Australia, with a total capacity of 453 MW. The wind farm, which was completed in 2020, features 123 turbines and is capable of powering more than 200,000 homes.
This development marks a significant step towards Queensland's goal of achieving 50% renewable energy by 2030. The project has created hundreds of construction and operational jobs, providing an economic boost to the local area. Coopers Gap is also part of a broader push to expand renewable energy in Queensland and reduce the state’s reliance on fossil fuels.
Granville Harbour Wind Farm (Tasmania)
Situated on the west coast of Tasmania, Granville Harbour Wind Farm is a major renewable energy project with a capacity of 112 MW. This wind farm consists of 33 turbines and was completed in 2021. It is part of Tasmania's broader goal to achieve 100% renewable energy generation, leveraging the state's abundant wind resources.
The Granville Harbour Wind Farm produces enough electricity to power around 70,000 homes annually and supports the local economy by providing jobs in both construction and ongoing operations. With the growing importance of Tasmania’s renewable energy exports, Granville Harbour plays a key role in the state’s energy mix.
10 economic and environmental advantages of wind energy
- Lower electricity costs: Wind energy is one of the cheapest forms of new power generation in Australia. As technology improves and more wind farms are built, the cost of wind power continues to fall.
- Job creation: The wind energy sector creates jobs in manufacturing, construction, operation, and maintenance. Thousands of Australians are employed in wind energy-related industries, boosting the economy.
- Energy independence: By generating electricity from domestic sources like wind, Australia can reduce its reliance on imported fossil fuels, making the country more energy secure.
- Grid stability: Wind power contributes to grid stability by diversifying the energy mix and reducing dependency on fossil fuels, which can be subject to price volatility.
- Rural development: Wind farms provide economic benefits to rural areas, including jobs, local business opportunities, and land lease payments to farmers.
- Investment in infrastructure: Wind energy projects often lead to the development of infrastructure in rural and remote areas, including roads, transmission lines, and other utilities.
- Support for renewable energy goals: Wind energy plays a central role in Australia’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and meeting renewable energy targets.
- Resilience to climate change: Wind farms are more resilient to extreme weather events compared to traditional power plants, which can be vulnerable to natural disasters.
- Minimal environmental impact: Wind farms, when properly sited, have relatively low environmental impact compared to other forms of power generation like coal or gas-fired plants.
- Reduced need for landfills: Wind turbines have long lifespans, and their components can often be recycled, helping reduce the environmental impact of waste.
The future of wind energy in Australia: trends and developments
As Australia looks towards a cleaner, greener energy future, wind energy will continue to play a critical role. Here are some trends and developments to look out for in the coming years:
- Increasing offshore wind projects: Offshore wind energy is poised to become a major part of Australia’s energy mix, with offshore farms expected to generate vast amounts of renewable electricity. The Australian government is exploring offshore wind projects, particularly in regions like the Bass Strait and along the east coast.
- Advanced turbine technology: Wind turbine technology continues to improve, with larger turbines that can generate more power and smaller, more efficient blades being developed. These innovations will help further reduce costs and increase output.
- Energy storage integration: As the share of renewable energy grows, integrating energy storage technologies, such as batteries, with wind farms will help ensure a stable supply of power, even when the wind isn’t blowing.
- Government support: The Australian government is increasingly supporting renewable energy projects through incentives, grants, and policy frameworks designed to drive investment in wind energy.
- Expansion of grid infrastructure: As more wind farms come online, Australia will continue to invest in its energy infrastructure, ensuring that the electricity produced by wind farms can be efficiently distributed across the nation.
Talk to us about your energy needs
Wind energy is helping to shape Australia’s renewable energy future by providing a clean, sustainable, and cost-effective solution to power the nation. With numerous large-scale wind farms and cutting-edge projects under development, Australia is well-positioned to continue expanding its wind energy capacity.
If you want to learn more about how wind energy is transforming Australia’s energy landscape or if you’re interested in exploring renewable energy options for your home, speak to the team at Compare Energy today on 1300 790 106. Our experts can guide you to the best energy plans, helping you save money while supporting sustainable energy

